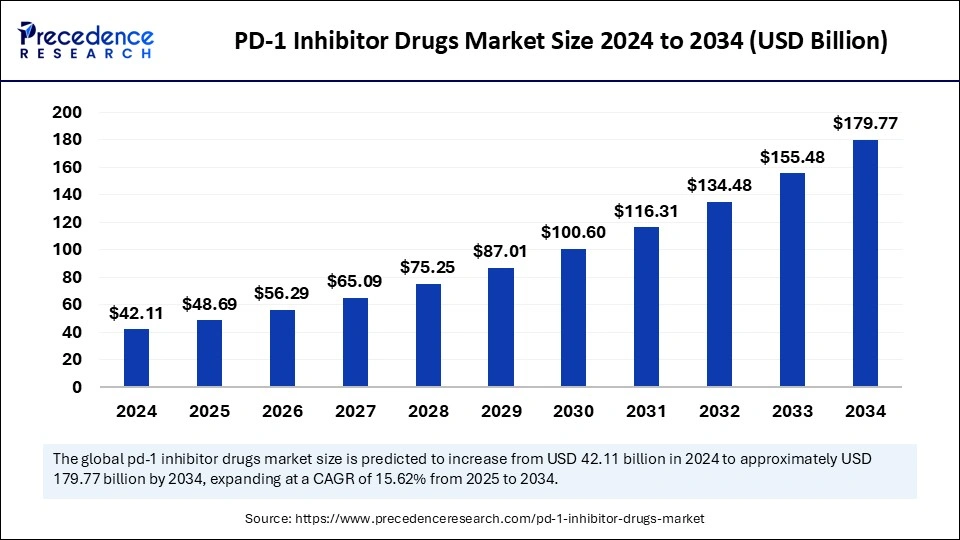
The global PD-1 inhibitor drugs market, valued at USD 42.11 billion in 2024, is projected to reach approximately USD 179.77 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 15.62% from 2025 to 2034.
PD-1 Inhibitor Drugs Market Key Takeaways
- North America dominated the PD-1 inhibitor drugs market in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to witness the fastest growth during the forecasted years.
- By drug type, the pembrolizumab segment contributed the largest share of the market in 2024.
- By drug type, the nivolumab segment is expected to show considerable growth in the forecast period.
- By indication, the non-small cell lung cancer segment dominated the market in 2024.
- By indication, the melanoma segment is anticipated to witness significant growth over the studied period.
- By distribution channel, the hospital pharmacies segment contributed the largest share of the market in 2024.
- By distribution channel, the online pharmacies segment is expected to show considerable growth in the forecast period.
The global PD-1 inhibitor drugs market is experiencing rapid expansion, driven by increasing demand for innovative cancer treatments and immunotherapies. PD-1 inhibitors, or programmed death-1 inhibitors, are a class of immunotherapy drugs designed to block the PD-1 protein on T-cells, thereby enhancing the immune system’s ability to detect and destroy cancer cells. These drugs have revolutionized cancer treatment, offering hope for patients with various malignancies, including melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, renal cell carcinoma, and Hodgkin lymphoma.
The growing prevalence of cancer worldwide, coupled with advances in biotechnology and personalized medicine, has significantly boosted the demand for PD-1 inhibitors. Pharmaceutical companies are heavily investing in research and development (R&D) to expand the applications of these drugs beyond oncology, exploring their potential in autoimmune diseases and chronic infections. As more clinical trials demonstrate the efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors across a broader range of conditions, the market is expected to witness substantial growth over the next decade.
Government initiatives promoting cancer research, increasing healthcare expenditures, and the rising adoption of immunotherapy as a standard treatment further contribute to the market’s expansion. With the introduction of biosimilars and combination therapies, PD-1 inhibitors are becoming more accessible to patients worldwide. However, the high cost of these therapies, along with regulatory challenges and potential adverse effects, remains a hurdle for widespread adoption. Despite these obstacles, the PD-1 inhibitor drugs market is poised for remarkable growth, with leading pharmaceutical companies continuously working to improve efficacy, safety, and affordability.
Sample Link: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/sample/5718
Key Drivers
One of the primary drivers of the PD-1 inhibitor drugs market is the rising incidence of cancer across the globe. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that cancer cases will continue to rise due to aging populations, environmental factors, and lifestyle changes. Traditional treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy often come with significant side effects and limited efficacy, making immunotherapy, particularly PD-1 inhibitors, an attractive alternative. These drugs offer targeted and more effective treatment options with fewer adverse effects compared to conventional therapies.
The growing acceptance of immunotherapy as a preferred cancer treatment modality has fueled investments in clinical research and drug development. Leading pharmaceutical companies such as Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Roche are actively engaged in developing next-generation PD-1 inhibitors with enhanced efficacy and broader applications. Combination therapies, where PD-1 inhibitors are used alongside chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or other immunotherapies, have shown promising results, further boosting market growth.
Regulatory approvals and fast-track designations from agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have accelerated the development and commercialization of PD-1 inhibitors. Governments and healthcare organizations are also supporting immunotherapy initiatives through funding programs, increasing patient access to these life-saving treatments. Furthermore, advancements in biomarker research have improved patient selection criteria, ensuring that PD-1 inhibitors are prescribed to individuals most likely to benefit from the therapy.
Opportunities
The expanding indications for PD-1 inhibitors beyond oncology present a significant opportunity for market growth. While these drugs are primarily used for cancer treatment, ongoing research suggests they may be effective in treating autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and type 1 diabetes. Clinical trials exploring the role of PD-1 inhibitors in infectious diseases, including chronic viral infections like hepatitis B and HIV, are also opening new avenues for market expansion.
Another major opportunity lies in the development of biosimilars, which can make PD-1 inhibitors more affordable and accessible to a larger patient population. The high cost of branded PD-1 inhibitors has been a barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in emerging markets. Biosimilars have the potential to address this challenge by offering cost-effective alternatives while maintaining comparable efficacy and safety profiles.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in drug discovery and clinical trials is expected to accelerate the development of new PD-1 inhibitors. AI-driven predictive models can help identify potential drug candidates more efficiently, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional drug development processes. Additionally, AI-powered diagnostics can enhance patient selection for PD-1 inhibitor therapies, ensuring better treatment outcomes.
Geographic expansion into emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, also presents significant growth opportunities. Rising healthcare expenditures, improving healthcare infrastructure, and increasing awareness of immunotherapy in these regions are driving demand for PD-1 inhibitors. Pharmaceutical companies are actively collaborating with local healthcare providers and governments to expand market reach and address unmet medical needs.
Challenges
Despite the promising growth prospects, the PD-1 inhibitor drugs market faces several challenges. One of the biggest obstacles is the high cost of these therapies, which limits patient access, especially in developing countries. PD-1 inhibitors are among the most expensive cancer treatments, with annual costs often exceeding $100,000 per patient. While insurance coverage and government subsidies help alleviate some financial burdens, cost remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption.
Regulatory challenges also pose hurdles for market expansion. The approval process for PD-1 inhibitors is complex and varies across different regions. Stringent regulatory requirements, including extensive clinical trials and post-marketing surveillance, can delay product launches and increase development costs. Additionally, variations in reimbursement policies across countries impact market penetration, as not all healthcare systems provide full coverage for these expensive therapies.
Another challenge is the potential for adverse effects associated with PD-1 inhibitors. While these drugs are generally well-tolerated, they can trigger immune-related side effects, including inflammation of the lungs, liver, intestines, and endocrine glands. Managing these adverse effects requires careful monitoring and may necessitate discontinuation of treatment in some cases. Addressing these safety concerns through improved drug formulations and combination therapies remains a priority for pharmaceutical companies.
The increasing competition in the PD-1 inhibitor market also presents challenges. While established players dominate the market, new entrants and biosimilar manufacturers are intensifying competition. The introduction of next-generation immunotherapies, including PD-L1 inhibitors and CAR-T cell therapies, further adds to the competitive landscape. Companies must continuously innovate and differentiate their products to maintain market share.
Regional Insights
North America remains the dominant market for PD-1 inhibitors, driven by high cancer prevalence, strong healthcare infrastructure, and significant R&D investments. The United States, in particular, accounts for the largest market share, with the presence of major pharmaceutical companies and extensive clinical trial activities. The FDA’s proactive approach to approving innovative immunotherapies has also contributed to market growth in the region.
Europe is another major market for PD-1 inhibitors, with countries like Germany, the United Kingdom, and France leading the adoption of immunotherapy. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has granted approvals for several PD-1 inhibitors, and national healthcare systems are increasingly incorporating these drugs into standard treatment protocols. However, differences in reimbursement policies across European countries can impact market accessibility.
The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a significant growth market for PD-1 inhibitors, driven by increasing cancer cases, improving healthcare infrastructure, and rising healthcare expenditures. China, in particular, is witnessing rapid market expansion, with domestic pharmaceutical companies actively developing and commercializing PD-1 inhibitors. Japan and South Korea are also key players in the region, with strong government support for immunotherapy research.
Latin America and the Middle East & Africa are relatively nascent markets for PD-1 inhibitors but hold immense growth potential. Increasing awareness about immunotherapy, government initiatives to improve cancer treatment, and collaborations with global pharmaceutical companies are expected to drive market growth in these regions. However, affordability and access to advanced treatments remain key challenges.
Don’t Miss Out: Solid Tumor Cancer Treatment Market
Market Key Players
- Akeso Inc.
- Alphamab Oncology
- Amgen Inc.
- AstraZeneca Plc
- BeiGene Ltd.
- Bristol Myers Squibb Co.
- Chia Tai Tianqing Pharmaceutical Group Co. Ltd.
- Eli Lilly and Co.
Recent News
Several recent developments have shaped the PD-1 inhibitor drugs market. The approval of new PD-1 inhibitors and expanded indications for existing drugs have broadened treatment options for patients. Pharmaceutical giants like Merck and Bristol-Myers Squibb continue to report strong sales growth for their flagship PD-1 inhibitors, Keytruda and Opdivo, respectively.
Research into combination therapies has yielded promising results, with studies demonstrating improved survival rates when PD-1 inhibitors are combined with other cancer treatments. Additionally, the emergence of biosimilars is expected to increase market competition and drive down costs, making PD-1 inhibitors more accessible to patients worldwide.
As advancements in immunotherapy continue to evolve, the PD-1 inhibitor drugs market is poised for significant growth. With ongoing R&D efforts, expanding applications, and increasing patient demand, these life-changing drugs will remain at the forefront of cancer treatment for years to come.
Market Segmentation
By Drug Type
- Pembrolizumab
- Nivolumab
- Cemiplimab
- Dostarlimab
- Others
By Indication
- Melanoma
- Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Kidney Cancer
- Head And Neck Cancers
- Stomach Cancer
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa